Introduction
Consonant Blends are taught in Milestone 6 and 7 of English Nali-Kali Level-2. Here, the students will learn how to combine consonants L, R, and S with other letters to form blended sounds.
In milestones 2 & 3, we covered the consonant combination sounds that come at the end of words. Just like NG, CK, and LL come at the end of a word, the blends introduced in milestones 6 & 7 come at the beginning of the word.
A point to remember is that you can usually hear each sound distinctly in the blended words and they are taught as a single unit with both sounds being heard. However, the first sound is usually stronger than the second.
{tocify} $title={Table of Contents}
In milestone 6, students are introduced to four and five-letter words, where when the letters 'L' and letter 'R' join with many other consonants to form blended sounds.
In milestone 7 is covered with consonant combinations when the letter 'S' joins a number of letters to form sounds that can occur at the beginning, middle or end of words.
- The common combinations with the L sound are: BL / CL / FL / GL / PL /
- The common combinations with the R sound are: BR / CR / DR / FR / GR / PR / TR /
- The common combinations with the S sound are: SC / SK / SL / SM / SN / SP / SW /
Teaching the Blends with 'L'
The first set of sounds taught are those when L is placed next to the letters B, C, F, G, and P. Care is to be taken to ensure that both the sounds are clearly heard when the letters are blended but the first sound is stronger.
 |
| Blends of 'L' |
Revision Step: Begin by revising the sounds of the letters B C F G and P Bring out the flashcards for each of the letters and place them in front and ask students to sound out the letters.
Step 1: Introducing the Blend
Tell students that in English we sometimes add 'L' to these letters. place the flashcard with 'L' next to the 'B' (or as in
milestone 2 you can hold the flashcard in each hand and bring them together slowly sounding out each sound and the blended sound
'bl' when the cards come together. Explain that when we do this, the letters say both the sounds together. Make sure that both the 'B' and 'L' sounds are clearly heard. Ask students to repeat after you.
Now take the flashcard 'C' and place it next to 'L'. Ask the student to sound out the two words. Repeat the process with the letters F, G, and P.
Step 2: Forming Word Families
Take the combination bl and add ACK, and ask children to sound out the combination word 'black'.
Step 3: Forming and Reading Words
Tell students that they can now do the same with other letters. Place the cl, fl, gl, and pl in a row (or write them on the wall slate) and form the words BLUE / BLIND / CLIP / CLAP / CLOSE / CLIMB / FLAG / FLY / FLOAT / FLOOD / GLUE / GLASS / GLOW / PLUG / PLAN / PLUG / PLATE.
As you go along allow students to sound out each of the words. Initially, encourage students by asking questions such as “what is the sound of CL”? What happens when IP is added to it? what is the sound? “Yes CLIP”.
As you move on to the 4th or 5th word allow the student/s to sound each blend and word family or long vowel/syllable as you write it. If the student has a problem underlines the syllable to help students understand such as GL-ASS. Be patient, and do not rush in with the answer. Ask students they know the meaning of the words. Tell them if they do not.
Step 4: Reading and Writing Words
Go to card 87 of the workbook. Ask children to read the words on the card and then recognize the pictures in card 88, fill in the letters and read them.
 |
Card No.88
|
Related: How to teach Grammar Concept in EnglishStep 5: Reading New Words
In the last 2 cards of 88 (88.4 and 88.5) students read words without picture clues. The words have to be sounded out and read using many of the rules of long vowel sounds and consonant blends they have learnt till now. Allow them to do the sounding out by themselves. Give them time to do the reading by themselves and come to you for a review. Once they can decode the words allow them to write them.
 |
Students read words without picture clues
|
Step 6: Read Sentences
Now move to activity 4 on sentence reading. Work with students on the first sentence allowing them to read each word and explain its meaning to you (they should be able to read all the words). Then allow them to do the remaining sentences working singly or in pairs to complete this exercise and then come to you for a review.
 |
| Activity 4: Read Sentences |
Teaching the Blends with 'R'
 |
| Blends of 'R' |
Step 1: Introducing the Blend
Place or write B&R next to each other or hold them in each hand and bring them slowly together sounding out each letter and say br… making sure that each sound is heard but B is stronger.
Step 2: Joining Word Families
Use the BR combination with vowels combinations or word families. Write the following on the board and get students to read the syllabic sounds BR-ICK / BR-OOM / BR-AIN / BR-OWN / and ask students to read the sounds produced.
Step 3: Forming Words
Now write the words CROW/DROP /FROG/ PRAY/TREE/ and let students read it as you write. Do not hurry students.
Step 4: Reading Words and Picture Words
(Activity 6, Card 91.1)
 |
| Reading picture words |
The word reading exercise is done independently by students. Allow students to decode each word by themselves. They now have enough phonetic knowledge to start reading longer words. When students come back to read to you explain the meaning of the words they do not know.
Step 5: Reading Words Without Clues
(Activity 6, Card 91.2)
Students read the words and come for a review. They can then practice writing the words in the workbook.
 |
| Reading words without clues |
Step 6: Sentence Reading
(Activity 8, Card 92)
The sentence reading exercise (should be done by the students themselves as these can be read by applying the rules of decoding that they have learnt.
 |
| Sentence Reading |
Allow children to read the first sentence with you. they then read the sentences ticking off the sentences they can read. When they finish reading any 10 of the 20 sentences, they come to you for a review. (this also helps to check which are the easiest sentences they can read). Students may make mistakes, and these should be corrected as they read them out to you.
Story-based Exercises
Identifying Sight Words
 |
| Identifying sight words |
Activity 10, Card 94: the sight words have already been introduced and revised in the oral class. Students are expected to try and read the passage and underline the sight words. They practice writing the words in the workbook (activity 11, Card 95) and complete the practice exercises in activity 12 (card 96).
Reading Story Sentences
Activity 13, Card 97: Students are expected to read the sentences by themselves. In order to read the sentences, students should know the keywords that would have been explained to them when the story was read. The key sentences are also read out to the children and explained during the storytelling session. Most of the words can also be decoded. Follow the process given below:
- wherever possible allow students to work together in pairs.
- sound out the unknown words (this can also be done by underlining the syllables and sounding them out (traf-fic)
- understand the context of the sentence and guess the words they cannot read yet.
- allow them to underline the words they cannot read and come to you where they can be helped to attack unknown words by understanding the context
The main point here is for the teacher to show patience. It is easy to be tempted to read the sentences and get children to read after you and learn it by heart. Teachers are advised not to do this. These are known sentences and students can decode most of the words and guess the remaining words.
Unjumble Words
Activity 14: It requires children to unjumble words. This is a more difficult exercise because children have to know the possible words like glass, tree, class, etc. before they can do it but most of the words are already known. Children can be helped to do this exercise as shown below:
 |
| Unjumble words - activity 14 |
Choose an easy word like "OWRC". Explain to children that the first step is to place the blend together. The blend here is 'CR'. Once this is done the 'OW' can be placed easily. Allow children to do the exercises by delinking the blend and then arranging the remaining words.
Activity 15 is simple if children know the words for the pictures. Allow children to do the exercise on their own.
Teaching the Blends with 'S'
The letter S can form blended sounds with C, K, L, M, N, P, Q, T, & W. Though S blends often do come at the beginning or middle of words, but they can also appear at the end of words. These are the 'SK', 'SP', 'ST' blends of which the 'SK' and 'ST' (covered in
milestone 3) is more common. The process for teaching 'S' blends is the same as that for teaching the 'L' and 'R' blends. Follow the steps below for teaching 'S' blends:
Step 1: Teach the 'S' Blends
Follow the same steps as in teaching the blends of 'L' and 'R'. Help students to first form the blended sound using the 'S' letter with C, L, M, P, K, P, & W.
Step 2:
Students learn to sound out syllables such as SC-OO- / SLA / SMA. By now this step would be easy for students and you can quickly move to step 3.
Step 3: Reading Words
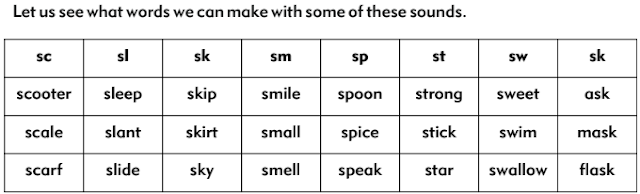
Form words SC-OO-TER / SC-ALE / SCARF / SLEE P / SLANT /SLIDE / SKIP /SKIRT /SKY / SMILE /SMALL/SMELL/ SPOON/SPICE/ SPEAK / STRONG / STICK / STAR / SWEET / SWIM
/ SWALLOW / ASK / MASK / FLASK.
Note that the words are becoming longer and requiring many more vowel combinations taught in milestones 4 and 5. If the teacher is working with a single child, he/she should try to make him/her read at least one word from each combination. Resist the temptation of jumping straight to step 4 as students have to see the words being written syllable by syllable.
Step 4: Reading and Writing Words
This step allows students to read the words. As you can see these have either all or partially already been covered by the teacher in step 3 and then the picture reading in activity 2.
$ads={2}Step 5: Reading Words Without Clues
Students read the words without picture clues independently many of which are a repeat of words already taught.
Step 6: Sentence Reading
Activity 4 doubles up both as a reading exercise as well as a grammar lesson on opposites. Begin by explaining the meaning of the word opposite and explain the meaning of the first sentence. the sentences are repetitive so students can focus on 2 words in each sentence. Many of these include other blends (climb, ground, blouse, etc.)
Practice Exercise
This (Activity 5) gets a bit more complicated. Activity 5 is a vocabulary exercise. Students must know the meaning of the words given in the box. They must also be able to read and understand the meaning of the sentences that give the clue. This exercise can be done in 2 steps. As a first step allow students to translate the words in the box into their mother tongue. They can write these down in the workbook or notebook.
Ask students to read and explain the sentences that provide the clue (actions we can do in water or actions birds do in the sky, etc.). Action is a difficult word and may have to be explained and understood as a sight word.
Story-based Exercises
Activity 6 -10 include sight word exercises and reading story sentences and activity 13 which is a reading grade 1 storybook should be done independently. By now students have enough phonic knowledge to decode most of the words.
Summary
- The most common blended sounds are obtained when L and R join with other letters.
- L and R blended sounds are usually found at the beginning or the middle of words.
- The sound of these blends can be heard distinctly. Therefore they are taught as a single unit with both sounds.
- The common combinations with the L sound are BL/CL/ FL/ GL/ PL
- The common combinations with the R sound are BR/CR/DR/FR/ GR/ PR/TR
- The common combinations with the S sound are SC/ SL/ SK at the beginning of the word/ SM/SP/ ST/ SW.
Reading and writing of words with R, L and S blends are taught in a logical manner using 4 activities:- Reading with picture and sound association
- Reading with a sound association
- Say and write activity
- Reading sentences with these words.
- Students are then introduced to some more sight words
- They read these sight words in context while they read the story of the theme.
--------
Credits: Samagra Shikshana Karnataka and UNICEF{alertInfo}